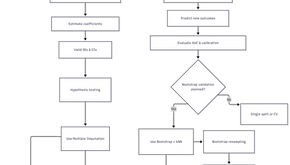
Why Missing Data Requires Both Imputation [Bootstrap then kNN] and Bootstrap [again] Internal Validation
First: fix one wrong mental picture I am thinking: “If complete data can do bootstrap once,missing data must do bootstrap twice → this feels like cheating / overkill.” This feeling comes from counting datasets , but internal validation is not about counting datasets . 👉 Internal validation is about ONE comparison : Was the model evaluated on data it was NOT trained on? Everything else is bookkeeping. Case 1 COMPLETE DATA (no missing) ❓ What is the correct internal validatio

Internal Validation with Bootstrap, kNN Imputation, and Fractional Polynomial Models [Thai]
(กรณี kNN imputation หลายชุด + Fractional Polynomial + Bootstrap) บทนำ: เรากำลังพยายามตอบคำถามอะไร? ในการพัฒนา prediction model คำถามสำคัญไม่ใช่แค่ว่า “โมเดล fit กับข้อมูลเราได้ดีแค่ไหน?” แต่คือ “โมเดลนี้ overfit แค่ไหนและถ้าเอาไปใช้กับคนใหม่ประสิทธิภาพจะลดลงเท่าไร?” การตอบคำถามนี้เรียกว่า Internal Validation บริบทของงานนี้ (Your exact problem) งานนี้มีความซับซ้อน 3 ชั้นพร้อมกัน: Missing data จำนวนมาก → ใช้ Boostrap before kNN single imputation ซ้ำหลายครั้ง → ได้ imputed dat

Handling Missing Data in Clinical Prediction Models: Bootstrap kNN vs Multiple Imputation
Overview Missing data are common in clinical datasets and must be handled carefully to avoid biased estimates, inflated performance, and invalid inference. In this study, missing values were addressed using k-nearest neighbor (kNN) imputation as an alternative to multiple imputation (MI) , followed by bootstrap-based internal validation of a diagnostic prediction model for gastrointestinal malignancy. This section describes the theoretical justification , practical implemen

Reading Bioinformatics / Precision Medicine Papers Systematically: EDPC Framework: Etiological, Discovery, Predictive, Confirmatory in Precision Medicine
Etiological • Discovery • Predictive • Confirmatory (EDPC) Precision medicine papers often look similar (omics + fancy plots), but they can be doing four very different jobs . Your slide deck defines these four objectives clearly: Etiological, Discovery, Predictive, Confirmatory . If you misclassify the objective, you will misread the results (e.g., treating “discovery” as “prediction”, or treating “prediction” as “clinical utility”). The EDPC map (what kind of paper is this

How to Choose Statistical Coefficients for Each Type of Reliability
Summary Table: Types of Reliability & Statistical Coefficients Reliability Type Purpose Data Type Statistical Coefficients (Named Statistics) 1. Test–Retest Reliability Measures stability over time (same test, two occasions) Continuous • Pearson r • Spearman ρ (ordinal or non-normal) • ICC (Intraclass Correlation Coefficient) • CCC (Concordance Correlation Coefficient) Ordinal • Spearman ρ • Weighted Cohen’s kappa Nominal / Dichotomous • Cohen’s kappa (κ) — Coeffici

How to Find Function Origins & Namespace Discipline in RStudio
1. Base R Functions Require No Library Some functions—such as paste0(), mean(), round(), factor()—belong to base R , which loads automatically. To verify: getAnywhere("paste0") Typical output: A single object matching ‘paste0’ was found It was found in: package:base Therefore: paste0() → base package → no library() required . 2. Determine the Origin of Any Function R exposes two powerful tools for function lookup. Method 1 — getAnywhere() Works even for hidden or S3/S4 gene

A Beginner’s Guide to Python Environments (Miniconda vs. Anaconda)
Introduction A Beginner’s Guide to Python Environments A clean, practical introduction for new programmers, researchers, and CECS students Managing Python environments is one of the most important early skills for anyone entering programming, data science, or clinical statistics. Many beginners underestimate this topic—until they face problems such as: “ModuleNotFoundError: package not found” “This function works on my laptop but not on the lab computer.” “Upgrading pandas br

Effect Size, MCID/CID, and Sample Size Relevance
1. Effect Size: The Foundation of Clinical Interpretation Effect size (ES) is the magnitude of difference or association between groups, exposures, treatments, or predictors. It is the central component of all DEPTh areas (diagnosis, etiology, prognosis, therapeutic, methodologic). “Always interpret effect size + 95% CI, not p-values alone.” Common Effect Size Metrics by Research Type DEPTh Type Effect Size Metrics Therapeutic Risk Ratio, Risk Difference, Mean Difference, H

Muscle Cramps (ตะคริว): Causes, Management, and When to Worry
1. Definition A muscle cramp is a sudden, painful, involuntary contraction of a muscle or muscle group, most commonly affecting the calves , feet , hamstrings , and sometimes hands or abdomen. Most cases are benign and arise from neuromuscular irritability due to electrolyte imbalance, dehydration, or muscle fatigue. 2. Epidemiology Very common: affects up to 60% of adults . More frequent at night and in elderly. Certain populations (pregnant women, athletes, diuretic users

Markdown vs Quarto: Choosing the Right Tool for Clinical Research
1. Overview: Markdown vs Quarto Markdown (MD) Markdown is a lightweight markup language used to format text into headings, bold/italic, lists, tables, code blocks, etc. Strengths: Simple syntax Ideal for README files, notes, tutorials Supported anywhere: GitHub, VS Code, RStudio, Stata logs (via dyndoc) Good for static documentation Limitations: Limited automation No native support for executing code chunks Cannot render statistical results automatically → Markdown alone is N

How to Report Model Updating (or Not) After Debray's External Validation: Examples, Tables & Templates
1. How they present external validation (text + tables) 1.1 Paper A – IDIOM model with updating Structure of the text Introduction Clinical background: iron deficiency anemia, GI malignancy. Introduces IDIOM model, original performance. States two aims : Describe prevalence/clinical characteristics of GI malignancy in Thai IDA patients Externally validate IDIOM and update it if needed. Methods Study design & patients (retrospective, single center, inclusion criteria, defini

Detrusor Underactivity (Underactive Bladder): Causes, Symptoms & Management [Bethanechol]
1. Definition Detrusor underactivity (DU) or Underactive Bladder (UAB) is a condition where the bladder muscle (detrusor) contracts too weakly and/or too briefly to empty the bladder completely during voiding. Formal urodynamic definition (ICS – International Continence Society): “A contraction of reduced strength and/or duration, resulting in prolonged bladder emptying and/or failure to achieve complete bladder emptying within a normal time span.” Clinically, you will see:

Seborrheic Dermatitis (Sebderm): Causes, Features & Treatment Overview
1. What is seborrheic dermatitis? Seborrheic dermatitis is a chronic, relapsing inflammatory skin disease affecting sebaceous (oil-rich) areas : Scalp Face (especially eyebrows, nasolabial folds, glabella) Ears, presternal chest, upper back, body folds It’s strongly associated with Malassezia (yeast) , sebum, and abnormal immune response. Prevalence: about 1–3% of the general population , much higher in HIV and neurologic disease (e.g. Parkinson’s). 2. Pathophysiology (high-

Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
1. What Is IBS? Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is a chronic functional gastrointestinal disorder characterized by recurrent abdominal pain associated with changes in stool frequency and/or form , without structural or biochemical abnormalities on routine testing. In simple terms: The gut looks normal (on colonoscopy, imaging) but functions abnormally. 2. Epidemiology & Impact Prevalence: ~5–10% of the population worldwide, depending on criteria used. More common in: Fema

Stability: The Key to Trustworthy Clinical Prediction Models
Beyond Calibration: The Rise of Prediction Stability While calibration corrects the long-standing misconception that discrimination alone is sufficient, it does not answer a deeper structural question: “Can I trust the model to give the same predictions if the training sample had been slightly different?” This is the domain of Prediction Stability —a newly recognized, methodologically essential property of Clinical Prediction Models (CPMs), highlighted in modern CPM developme

Cohen’s Kappa vs Weighted Kappa: Measuring Agreement Beyond Chance
How to measure agreement beyond chance 1. Why do we need Kappa? When two raters (or two methods) classify patients into categories—for example: Fracture: yes / no CT severity: mild / moderate / severe ECG finding: normal / abnormal we want to know: Do they really agree, or are they just “lucky” to match by chance? Simple percent agreement (% of cases where both give the same category) is easy to understand but has a big limitation: If one category is very common (e.g., “no d

How Clinical Scores Are Built: From Logistic Coefficients to Point Systems
1. Where does a clinical score come from? Most modern scores come from a prediction model , usually: Logistic regression for binary outcomes (e.g. appendicitis: yes/no) Cox model for time-to-event (e.g. 10-year CVD risk) For a logistic model, the development team fits: Y = outcome (e.g. disease yes/no) Xj = predictors (e.g. fever, RLQ pain, WBC, etc.) α = intercept βj = log-odds coefficients Those βj are the true origin of the score. The score is just a simplified, rounded v

Agreement vs Reliability in Categorical Data: A Practical Guide for Clinical Researchers
1. Why do we care about reliability? When you design a clinical tool (score, scale, questionnaire, diagnostic classification), you usually have: Raters (people or systems making the judgment) Repeated measurements (same patient, same test, measured twice or more) Categorical outcomes (e.g. “present/absent”, “stage I/II/III”, “mild/moderate/severe”) You want to know: Agreement – Do raters give the same category? Reliability – Does the measurement reflect true differences